
Cooperative Learning Strategies (Slavin, 1990)
Cooperative Learning Visual Concept Diagram
Description
Cooperative learning can be described as means of providing opportunities for pupils to work together as a team in accomplishing a set of given objectives. It is collaborative in nature and focuses on individual accountability to team success. A major benefit of cooperative learning includes the nurturance and development of social interaction skills.
Principles of Project-based Learning
Cooperative learning as a teaching strategy relies on the following:
- Pupils are assigned to small groups or teams (ideally no more than 4 members in a group),
- Teams are comprised of pupils of different ability levels.
- The immediate intention is that each member of the "team" accepts the responsibility to achieve the goal(s) of instruction while helping any teammates who need assistance. Tasks or activities that are assigned can vary in nature depending on the grade level. The ultimate goal is to promote positive relationships and mutual respect among teammates, to foster accountability (both individual and group), and to provide a venue for problem solving as a team.
The more popular strategies used in cooperative learning include:
> Group Investigation
> STAD (Student Teams-Achievement Divisions)
> Jigsaw II
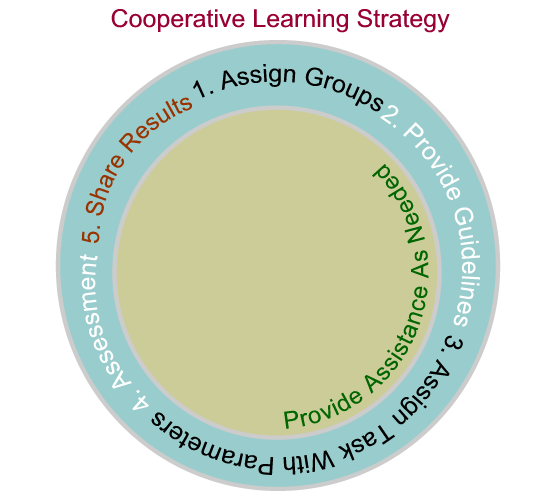
Procedures
- Assign groups according to different ability levels or backgrounds keeping each team as diverse as possible.
- Choose a cooperative learning strategy that the team will use to complete the task.
- Assign a task to be completed defining the parameters and clearly identifying the goals.
- Provide assistance when needed.
- Provide an evaluation checklist with points to determine progress in achieving team goals.
- Provide an opportunity for the team to share results of teamwork.